| [1] 王秋雁,何瑾,王晶晶,等.万古霉素不同给药方式所致肾毒性[J].中国医院药学杂志,2017,37(11):1108-1111.[2] 申庆荣,李刚,卢秋玉,等.万古霉素血药浓度的影响因素分析[J].中国抗生素杂志,2017,42(5):429-434.[3] 余方友,李美兰,林晓梅,等.万古霉素对金黄色葡萄球菌体外抗菌活性研究[J].中国微生态学杂志,2006,18(3):240-242.[4] 范倩,邓凡,乐春星,等.明胶/海藻酸钠复合微球的研究[J].化工新型材料, 2017,45(1):176-178.[5] 冀萍,陈哲,孙晓晨,等.明胶海绵颗粒和壳聚糖α,β-甘油磷酸凝胶微球在肺结核咯血应用中的对比[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(18):2876-2880.[6] 谭深,宋媛媛,张建安,等.聚乳酸载药微球的制备及改性的应用进展[J].化工新型材料,2015,43(9):231-233.[7] Sherwood JK, Riley SL, Palazzolo R, et al. A three-dimensional osteochondral composite scaffold for articular cartilage repair. Biomaterials. 2002;23(24):4739-4751.[8] Park TG. Degradation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: effect of copolymer composition. Biomaterials. 1995;16(15):1123-1130.[9] 罗宇燕,成晓岚,郭喆霏,等.微球中聚乳酸羟基乙酸共聚物浓度与微球结构、释药、降解的关系研究[J].中国药房, 2015,26(7):986-991.[10] 王飞.万古霉素局部微球注射治疗耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染性椎间盘炎的实验研究[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2013,6(6):519-525.[11] 王志斌,朱磊,王明波,等.自体微小颗粒骨载万古霉素复式微球治疗兔骨感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2017,39(2):126-130.[12] 刘冰,陈鹏.负载万古霉素纳米微球缓释系统的β-磷酸三钙修复感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2012,13(1):16-19.[13] 张姝江,李益丰,陈艺,等.万古霉素壳聚糖微球-大孔磷酸钙骨水泥支架的体外释放实验[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016,10(6):630-635.[14] 曹雪飞.3D打印β-磷酸三钙负载INH、RFP/PLGA缓释微球的生物安全性及成骨作用的研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2016.[15] 赵转霞, 刘哲鹏, 董堃华,等.奥曲肽长效生物可降解微球的制备及其分析方法研究[J].生物医学工程学进展, 2014,35(3):155-159.[16] 靳浩,吴诚,梅兴国.多指标综合评价法优选阿霉素微球的制备工艺及体内的初步考察[J].中国药学杂志, 2006,41(22):1723-1725.[17] 林凤云,罗易,何雄伟.恩替卡韦-PLGA缓释微球的处方优化及体外释药研究[J].中国药房,2016,27(25):3549-3552.[18] 刘华杰,李亚磊,魏娇,等.骨保护素-聚乳酸羟基乙酸缓释微球的制备及体外释药性能研究[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2017,52(11):1658-1662.[19] 段宏,樊瑜波,屠重棋,等.缓释bFGF微球的制备及微球对成骨细胞的作用[J].华西药学杂志,2007,22(3):259-262.[20] 柴雪,屈铁军,李伟,等.牛血清白蛋白乳酸-羟乙酸共聚物缓释微球制备工艺的优化[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2013,23(4):270-274.[21] 林丽,黄华,张涛,等.伊潘立酮长效缓释微球的制备及体外释药特性研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2014,36(3):274-277.[22] 刘启明,周岳,王明波,等.自体微小颗粒骨复合万古霉素缓释微球治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014,16(11):983-989.[23] 裴世成.正交试验优选α-细辛脑明胶微球制备工艺[J].中国药房, 2011, 22(47):4452-4453.[24] 谭红香,叶建东.PLGA包埋硫酸庆大霉素缓释微球的制备及体外释放行为[J].中国抗生素杂志,2007,32(11):682-684.[25] Woodard JR, Hilldore AJ, Lan SK, et al. The mechanical properties and osteoconductivity of hydroxyapatite bone scaffolds with multi-scale porosity. Biomaterials. 2007;28(1):45-54.[26] Teixeira S, Fernandes H, Leusink A, et al. In vivo evaluation of highly macroporous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(2):567-575. [27] Lu L, Zhang Q, Wootton D, et al. Biocompatibility and biodegradation studies of PCL/β-TCP bone tissue scaffold fabricated by structural porogen method. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(9):2217-2226. [28] 王小鹏,陈天宁.可降解高聚物PLGA降解溶蚀的仿真模型[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2012,28(2):174-178.[29] 万古霉素临床应用中国专家共识(2011版)[J].中国新药与临床杂志, 2011, 30(8):561-573.[30] 王翠红,栾婷,叶蕊,等.万古霉素血清谷浓度监测及临床应用分析[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2017,33(9):771-773,777.[31] 忻娜.超临界CO2抗溶剂法制备姜黄素及姜黄素-PLGA复合纳米颗粒[D].上海:上海交通大学,2014.[32] Malavia N, Reddy L, Szinai I, et al. Biodegradable sustained-release drug delivery systems fabricated using a dissolvable hydrogel template technology for the treatment of ocular indications. Inv Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(7):1296. |
.jpg)
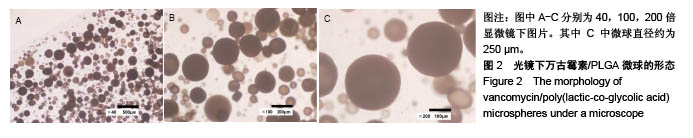

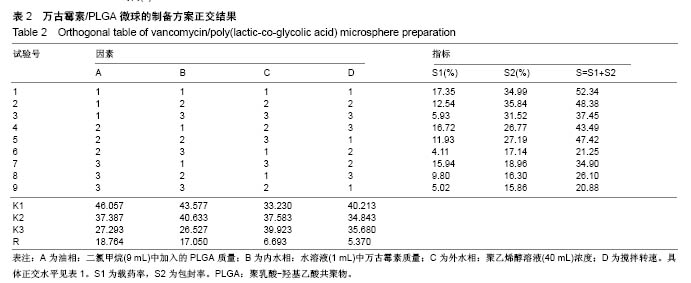

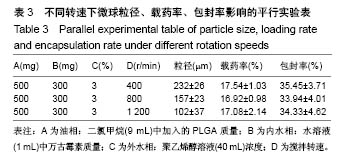
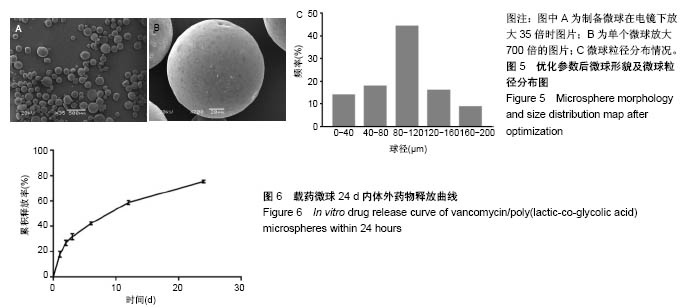


.jpg)
.jpg)